Latest News
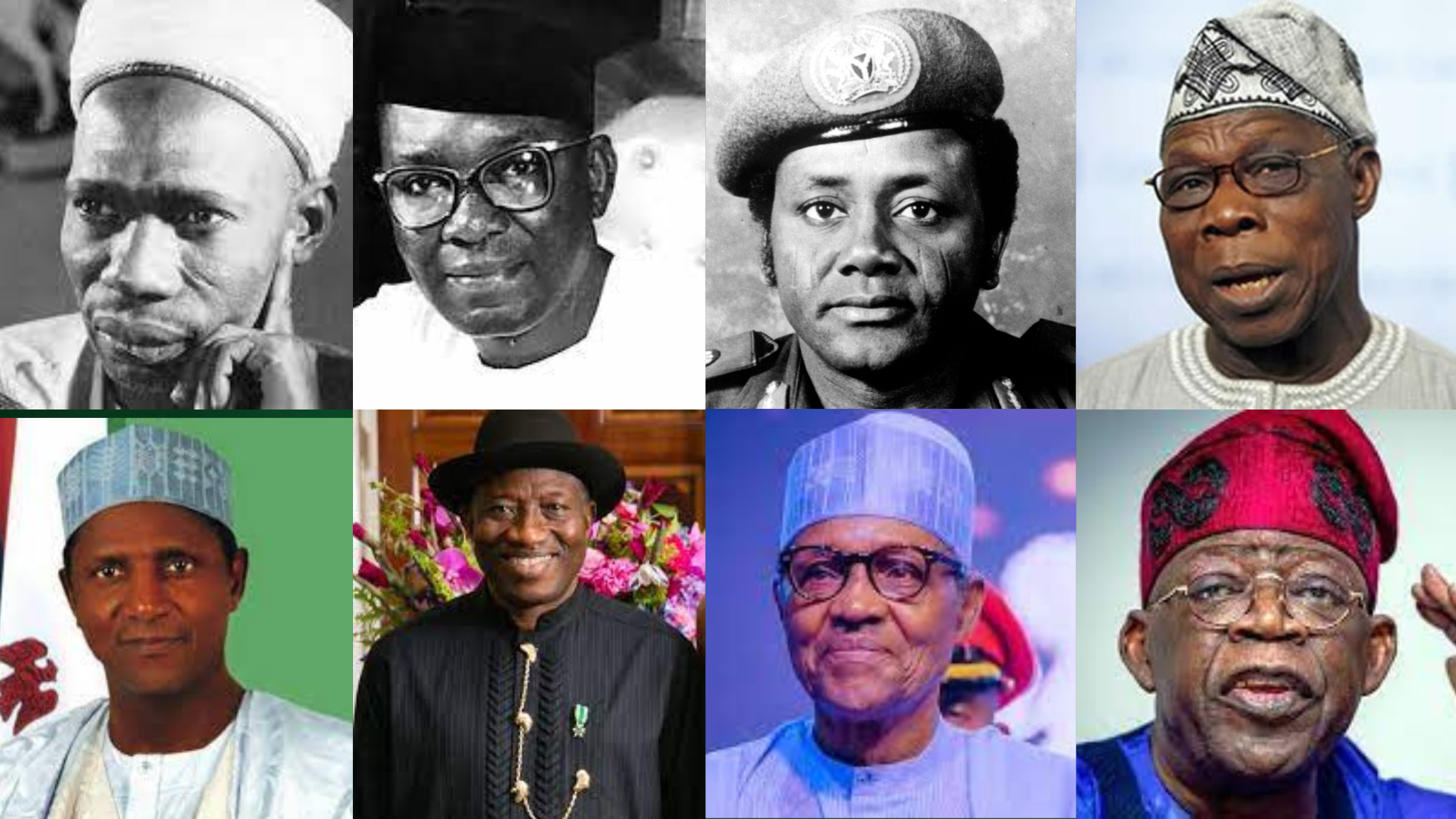
List Of Nigeria Presidents and Heads Of State
Nigeria has witnessed a succession of presidents, and heads of state, each playing a significant role in shaping the country’s political landscape

Nigeria, a country rich in blessings and opportunities, has been fortunate to have had exceptional individuals who dedicated their services to the nation.
Nigeria has witnessed a succession of presidents, and heads of state, each playing a significant role in shaping the country’s political landscape
In this article, RNN aims to provide a detailed list of Nigeria past presidents and head of state who have ruled Nigeria since its independence in 1960 until the present year of 2023. Along with their respective pictures and tenures, we will also highlight some of their notable achievements.
PRE-INDEPENDENCE ERA

COLONIAL RULE AND EARLY POLITICAL MOVEMENTS
Nigeria was controlled by the British Empire in the late 19th century, leading to colonial rule and the introduction of British systems. This had a significant impact on Nigeria’s society, politics, and economy.
However, it also sparked resistance and the formation of political movements, such as the Nigerian National Democratic Party and the National Council of Nigeria and the Cameroons, which fought for self-governance and independence. These movements raised awareness, challenged oppressive policies, and laid the foundation for Nigeria’s eventual independence.
These early political movements in Nigeria laid the groundwork for a unified struggle against colonial rule and played a crucial role in shaping the national consciousness. They raised awareness about the need for self-governance, challenged oppressive policies, and advocated for the rights of Nigerians.
KEY LEADERS AND ACTIVISTS IN THE PRE-INDEPENDENCE ERA
During Nigeria’s pre-independence era, influential leaders such as Herbert Macaulay, Nnamdi Azikiwe, Obafemi Awolowo, Funmilayo Ransome-Kuti, and Ahmadu Bello played crucial roles in shaping Nigeria’s path towards independence by advocating for the rights and interests of Nigerians, establishing political parties, fighting against colonial rule, and championing social welfare, women’s rights, and regional unity.
TRANSITION TO SELF-GOVERNANCE
The journey towards self-governance in Nigeria has been a long and arduous one. After Nigeria gained independent in 1960, Nigeria has been working towards establishing a stable and effective system of self-governance. Over the years, the country has undergone various political transitions, including military regimes and periods of civilian rule.
These transitions have shaped the political landscape of Nigeria and have played a crucial role in the country’s journey towards self-governance.
One of the significant milestones in Nigeria’s transition to self-governance was the return to civilian rule in 1999. After years of military dictatorship, Nigeria held democratic elections, and Olusegun Obasanjo became the first civilian president of the Fourth Republic. This marked a significant turning point in Nigeria’s political history and set the stage for a more inclusive and participatory form of governance.
To further enhance self-governance, Nigeria has been focused on improving transparency, accountability, and citizen participation.
NIGERIA FIRST REPUBLIC (1960-1966)
INDEPENDENCE AND THE EMERGENCE OF NIGERIA’S FIRST PRESIDENT
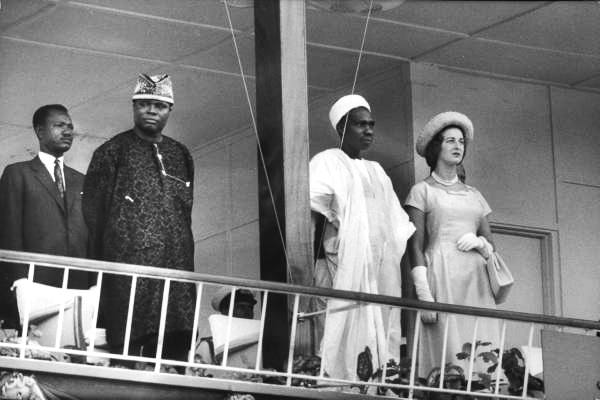

Nigeria had long been ruled by the British Empire, but in the mid-20th century, a desire for independence grew among the Nigerian people. Inspired by other African nations, they rallied for self-rule and freedom.
Key events and movements paved the way for Nigeria’s independence. The Nigerian Youth Movement, formed in 1933, played a crucial role in advocating for self-governance. Political parties like the National Council of Nigeria and the Cameroons (NCNC) and the Action Group (AG) further mobilized Nigerians in their quest for self-determination.
After years of struggle and negotiations, Nigeria finally gained independence on October 1, 1960. This momentous day was the result of the unwavering determination of Nigeria’s leaders and citizens. The entire nation rejoiced as they raised the Nigerian flag, symbolizing the birth of a free nation.
Emergence of Nigeria’s First President:
The attainment of independence and the inauguration of Nigeria’s first president were significant moments in the country’s history. They symbolized Nigeria’s transition from being ruled by a foreign power to governing themselves, setting the stage for future accomplishments and challenges.
In 1963, Nigeria adopted a new constitution and switched from a parliamentary system to a republic. This change allowed them to appoint their first president.
The emergence of Dr. Nnamdi Azikiwe as the first president stands as proof of the resilience and determination of the Nigerian people in their pursuit of a better future.
POLITICAL PARTIES AND THE CHALLENGES OF DEMOCRATIC GOVERNANCE
Democratic governance, despite its many benefits, is not without its challenges and one of the primary challenges is ensuring citizen participation. In a democratic system, the power ultimately rests with the people.
Lack of political awareness, apathy, and low voter turnout are common hurdles that impede effective democratic governance. Governments must work to educate and motivate citizens to actively participate in decision-making processes to ensure the system’s legitimacy.
Another significant challenge is the presence of political polarization. In democratic societies, diverse opinions and ideologies are expected and encouraged.
Additionally, external threats such as terrorism, cyber security, and foreign interference pose challenges to democratic governance. These threats can undermine stability, disrupt democratic processes, and erode public trust.
SUCCESSES AND FAILURE OF THE FIRST REPUBLIC
Nigeria’s First Republic, which lasted from 1963 to 1966, played a crucial role in the country’s journey towards independence and self-governance. This period witnessed both significant successes and unfortunate failures that shaped Nigeria’s political landscape.
The successes of Nigeria’s First Republic include gaining independence from British colonial rule and promoting education to improve literacy rates and socio-economic progress. However, the First Republic also faced challenges such as political instability and ethnic/regional tensions, which contributed to its failure.
Additionally, economic disparities persisted despite the growth experienced during the First Republic. This imbalance contributed to feelings of marginalization and inequality, further fueling social tensions and political instability.
MILITARY COUPS AND MILITARY RULE IN NIGERIA(1966-1979)
MAJOR COUPS AND THEIR IMPACT ON NIGERIA’S POLITICAL LANDSCAPE
In Nigeria, there were several significant coups that had lasting effects on the country. The first coup in 1966 overthrew the civilian government and led to a power struggle and eventually the Nigerian Civil War. The secession of the Biafra region in 1967 triggered a brutal civil war, highlighting ethnic tensions.
Another military coup in 1975 brought General Mohammed to power, who implemented reforms but was assassinated the following year. General Babangida’s regime from 1985 to 1993 was marked by political instability and the annulment of a free and fair election, leading to protests and loss of confidence in the government. Nigeria transitioned to democracy in 1999, but still faces challenges like corruption and social disparities.
THE RISE OF NIGERIA MILITARY RULERS AND THEIR POLICIES
During the period between 1966 and 1979, Nigeria witnessed a significant rise in military rulers taking control of the country’s government. This era marked a pivotal moment in Nigerian history, shaping the nation’s political landscape and leaving a lasting impact on its people.
The 1966 coup d’état in Nigeria marked the start of military rule, leading to a series of takeovers and political instability. General Yakubu Gowon emerged as the new leader, followed by the Nigerian Civil War in 1967. After the war, dissatisfaction with Gowon’s government grew, leading to another coup in 1975 by General Murtala Ramat Mohammed. Mohammed was later assassinated, and General Olusegun Obasanjo took over, introducing reforms but maintaining military rule.
The military regime in Nigeria accomplished several things. They preserved Nigeria’s unity by fighting the civil war. Military regime developed infrastructure by building roads, bridges, airports, and institutions and created more states, giving different ethnic groups self-determination.
This regime also established the National Youth Service Corps (N.Y.S.C.) to promote unity among ethnic groups and made positive changes to Nigeria’s foreign policy. Additionally, Gowon and Eyadema established the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
NIGERIA SECOND REPUBLIC (1979-1983)
RETURN OF CIVILIAN RULE AND THE ADOPTION OF A NEW CONSTISTUTION
Nigeria has transitioned from military rule to civilian rule, adopting a new constitution that ensures democratic governance and protects citizens’ rights and freedoms.
The new constitution promotes inclusivity, accountability, and the separation of powers. It guarantees fundamental rights, combats corruption, and encourages economic growth. While there are challenges ahead, this development is a milestone towards a prosperous and inclusive future. Nigeria must remain dedicated to upholding the constitution and addressing socio-economic disparities for a strong democracy.
ELECTIONS AND THE EMERGENCE OF THE SECOND PRESIDENT
In a historic turn of events, Nigeria has witnessed the emergence of its second president. This momentous occasion marks a significant milestone in the nation’s political landscape.
Nigeria has a new president, marking a significant moment in the country’s politics. After a closely contested election, the second president takes on the responsibility of leading Nigeria into a new era. Nigeria stands at a critical juncture, with immense opportunities and challenges, and the hopes of millions are placed on the second president to steer the country towards prosperity and progress. The Nigerian people are united in their belief that their chosen leader will lead them to a brighter future, filled with optimism and determination.
ACHIEVEMENTS AND CHALLENGES OF THE SECOND REPUBLIC
The Second Republic in Nigeria, which lasted from 1979 to 1983, was an important time in the country’s history. It marked a shift from military rule to civilian government, with hopes of bringing political stability and economic progress.
The government achieved notable successes during this period, such as adopting a new constitution that promoted democracy and protecting human rights. They also focused on diversifying the economy, improving education and healthcare, and expanding infrastructure.
However, the Second Republic faced challenges including political instability, corruption, and security issues. In 1983, a military coup led by General Muhammadu Buhari ended the Second Republic, setting back Nigeria’s democratic progress. Overall, the Second Republic made strides but also showed the difficulties of nation-building and the need for continued efforts to overcome obstacles.
RETURN OF MILITARY RULE IN NIGERIA(1983-1999)
THE BUHARI-IDIAGBON REGIME AND ITS POLICIES
In the 1980s, Nigeria faced corruption, economic instability, and declining public trust. The Buhari-Idiagbon regime took power in 1983 to address these issues. They focused on fighting corruption through the War Against Indiscipline campaign, implemented economic reforms through the Structural Adjustment Program, and improved national security with Operation Decree. They also aimed to restore Nigeria’s international standing and strengthen regional cooperation.
However, their strict policies and suspension of democratic institutions sparked criticism and dissatisfaction among Nigerians. Despite their impact, the regime ended in 1985 due to a military coup, leaving a lasting influence on Nigeria’s future governments and discussions on security, governance, and civil liberties.
THE BABANGIDA ERA AND THE TRANSITION PROGRAMS
The period from 1983 to 1999 in Nigeria was led by General Ibrahim Badamosi Babangida, who implemented political transition programs. His era had a lasting impact on Nigeria, shaping its political landscape. Babangida introduced the Economic Structural Adjustment Program (ESAP) to modernize the economy, but it resulted in economic hardships.
He also initiated a transition to civilian rule, but controversies and the annulment of the 1993 presidential election led to political instability. Despite setbacks, Babangida handed over power in 1999, marking the start of Nigeria’s Fourth Republic. The era had both positive and negative effects and is still a topic of discussion and evaluation.
THE ABACHA REGIME AND ITS CONTROVERSIAL RULE
The Abacha regime in Nigeria, led by General Sani Abacha from 1993 to 1998, was highly debated and controversial. It annulled a widely acclaimed presidential election, leading to protests and accusations of authoritarianism. Human rights violations, corruption, and embezzlement were widespread under Abacha’s rule.
Despite some supporters citing his anti-corruption stance and stability, the regime’s abuses overshadowed these arguments. After Abacha’s death, Nigeria transitioned to democracy, but the legacy of the regime remains influential, emphasizing the need for democracy, human rights, and combating corruption. Reflecting on the past and promoting accountability and democratic institutions can lead Nigeria towards a better future, moving beyond the contentious Abacha era.
FOURTH REPUBLIC (1999-PRESENT)
TRANSITION TO CIVILIAN RULE AND THE FOURTH CONSTITUTION
Nigeria transitioned from military to civilian rule in 1999, introducing the fourth constitution which aimed to establish democracy and protect citizens’ rights. The constitution decentralized power and separated it into three branches, ensuring checks and balances. It emphasized human rights, an independent judiciary, and has been amended over time.
The transition and constitution have fostered democracy, but challenges like corruption and inequality persist. They serve as important milestones for Nigeria’s history and provide a foundation for future development by upholding principles and promoting citizen participation.
ELECTIONS AND THE SUBSEQUENT PRESIDENTS/ HEAD OF STATE
Since 1999, Nigeria has had several elections that determined its Presidents. Obasanjo won in 1999 and 2003, focusing on reforms. Yar’Adua won in 2007 but faced health challenges. Jonathan took over and won in 2011, focusing on development.
Buhari won in 2015 and 2019, addressing corruption and security. The 2023 elections has decide the next leader, Chief Bola Ahmed Tinubu. These changes have shaped Nigeria’s political landscape and will continue to shape its future.
MAJOR ACHIEVEMENTS AND CHALLENGES OF THE FOURTH REPUBLIC
Nigeria’s Fourth Republic, starting in 1999, has seen successes like transitioning to democracy, stable economic growth, and anti-corruption measures. However, challenges of insecurity and inadequate infrastructure persist, requiring continued efforts to ensure a prosperous and secure nation for all Nigerians.
FULL LIST OF NIGERIA PRESIDENTS/ HEAD OF STATE
This article aims to provide a detailed list of Nigeria past presidents and head of state who have ruled Nigeria since its independence in 1960 until the present year of 2023. Along with their respective pictures and tenures, we will also highlight some of their notable achievements.
| NAME OF PRESIDENT/HEAD OF STATE | TYPE OF GOVERNMENT | Tenure (Year) |
| Abubakar Tafawa Balewa | Military | 1960-1963 |
| Nnamdi Azikwe | Military | 1963-1966 |
| Aguiyi Ironsi | Military | 1966 |
| Yakubu Gowon | Military | 1966-1975 |
| Murtala Rufai Mohammed | Military | 1975-1976 |
| Olusegun Aremu Obasanjo | Military | 1976-1979 |
| Alhaji Shehu Shagari | Military | 1979-1983 |
| Muhammadu Buhari | Military | 1983-1985 |
| Ibrahim Babangida | Military | 1985-1993 |
| Ernest Adegunle Shonekan | Military | 1993 |
| Sani Abacha | Military | 1993-1998 |
| Abdulsalami Abubakar | Military | 1998-1999 |
| Olusegun Aremu Obasanjo | Democratic | 1999-2007 |
| UmaruMusa Yar’Adua | Democratic | 2007-2010 |
| Goodluck Ebele Jonathan | Democratic | 2010-2015 |
| Muhammadu Buhari | Democratic | 2015 till date |
| Bola Ahmed Tinubu | Democratic | From May 29th 2023 |
1. Prime Minister Abubakar Tafawa Balewa (1960-1963)
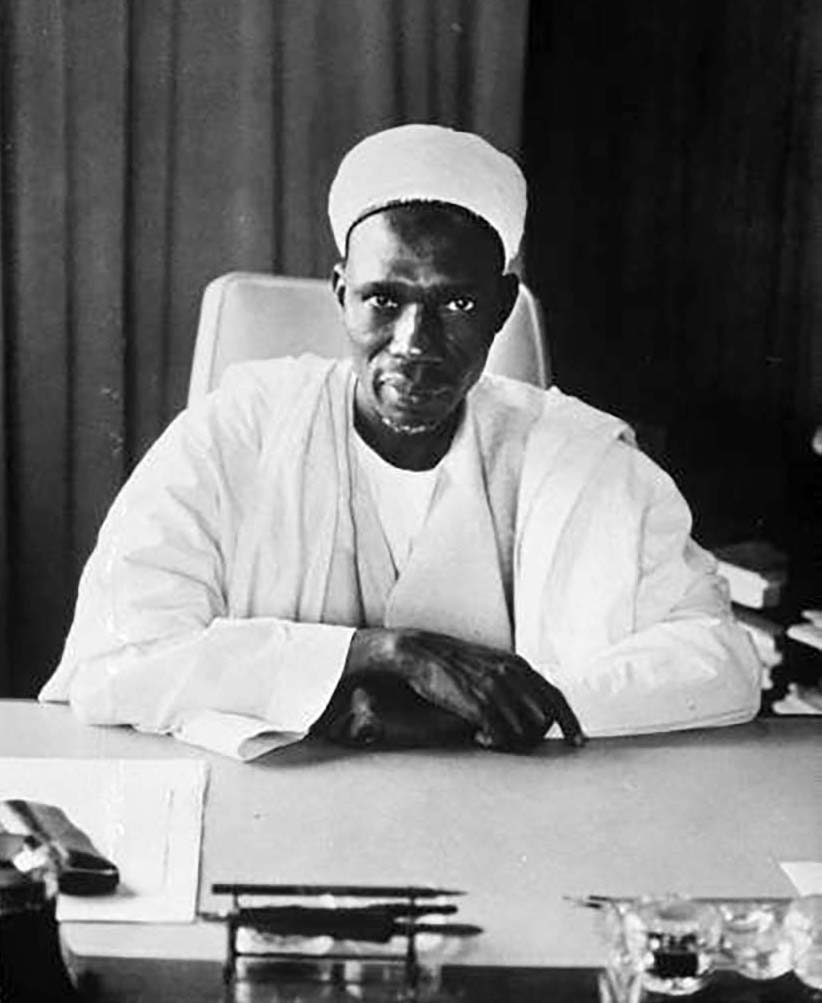

Sir Abubakar Tafawa Balewa, a Nigerian politician, played a significant role in the early days of Nigeria’s independence. Abubakar was born in December 1912, he served as Nigeria’s first and only prime minister.
After years of British colonial rule, Nigeria gained independence, and Sir Abubakar Tafawa Balewa became the first Prime Minister from 1960 to 1963, marking Nigeria’s transition to a republic.
One of Balewa’s notable contributions was his instrumental role in Nigeria’s attainment of independence from British colonial rule.
During his tenure, Balewa implemented several policies aimed at fostering economic growth and improving the living standards of Nigerians. He emphasized the importance of education and invested in infrastructure projects, such as road construction and the establishment of schools, to enhance the country’s development.
Balewa’s leadership style was characterized by his humility, wisdom, and dedication to public service. He was respected for his integrity and his ability to listen to the concerns of the people. His vision for Nigeria was centered on achieving progress through peaceful means and ensuring the welfare of all citizens.
Tragically, Balewa’s remarkable contributions were cut short when he was overthrown and assassinated in a military coup in January 1966. Nevertheless, his legacy as a visionary leader and advocate for Nigeria’s progress remains intact.
2. President Nnamdi Azikiwe (1963-1966)

Nnamdi Benjamin Azikiwe, widely known as “Zik,” was a prominent Nigerian statesman and political leader. Born on November 16, 1904, and passed away on May 11, 1996, he held the honorific title of GCFR PC.
Azikiwe was the first President of Nigeria after the nation transformed into an independent republic.
He had a successful career in publishing and then entered politics with Sir Herbert Macaulay. Together, they founded the National Council of Nigeria and Cameroon (NCNC), which eventually transformed into the National Council of Nigeria Citizens (NCNC).
During his tenure, Nigeria’s first constitution as a federal republic – the 1963 Constitution was declared. He served for three years from 1963 to 1966 until a military coup removed him from power.
Zik played a pivotal role in Nigeria’s history, serving as the country’s first ceremonial president. His leadership left a lasting impact on the nation.
3. Major-General Johnson Aguiyi-Ironsi (1966)
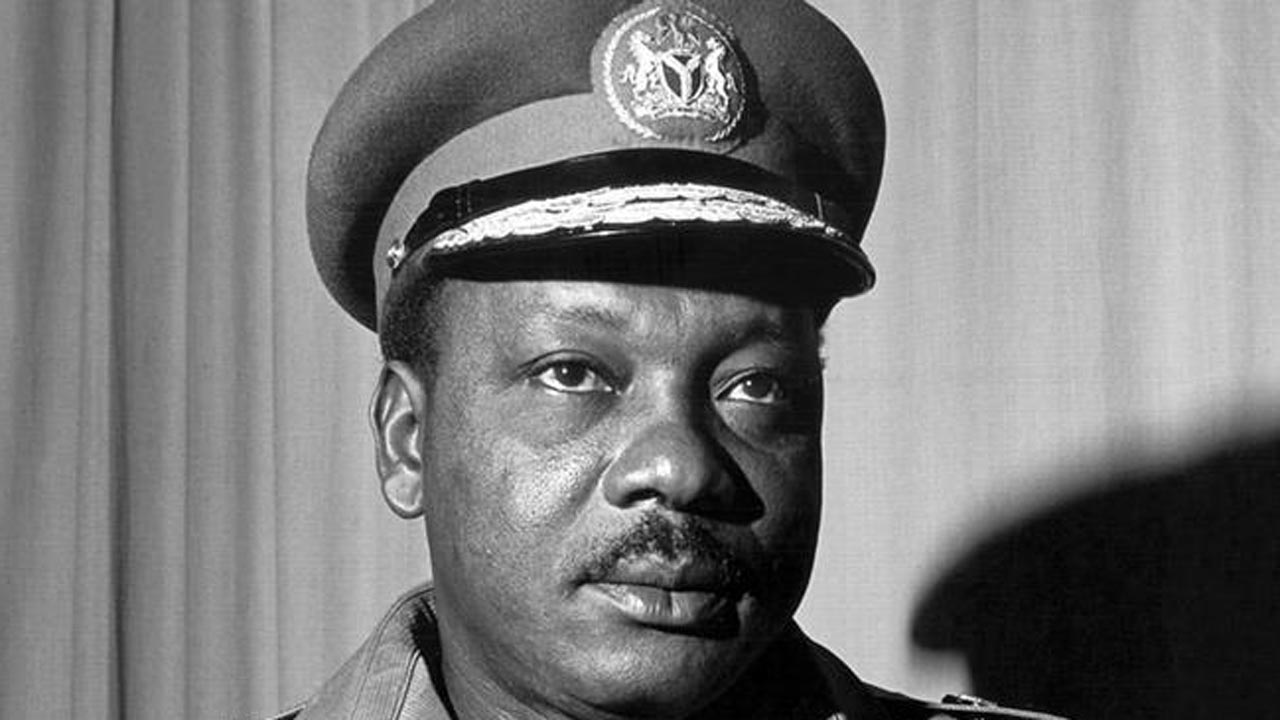

Major General Johnson Thomas Aguiyi-Ironsi, Nigeria’s first military Head of State, was born in 1924 in Umuahia, Abia State. He is the third president on the list of Nigerian Presidents.
He joined the Nigeria Army in 1942 as a private and was promoted to the rank of Major General in 1964. Aguiyi-Ironsi was a high-ranking officer in the Nigerian military and led the 1966 coup against Azikiwe’s government.
During his short tenure, Aguiyi-Ironsi issued several decrees. One of these was the Constitution Suspension and Amendment Decree No.1, which suspended most articles of the Constitution.
However, he did not interfere with sections of the constitution that protected fundamental human rights, freedom of expression, and conscience.
4. General Yakubu Gowon (1966-1975)

General Yakubu Gowon served as the head of state of Nigeria from 1966 to 1975. During his tenure, he played a significant role in the country’s history and oversaw various political and economic developments.
During his time in office, Gowon also implemented various economic policies aimed at promoting development and reducing poverty. He launched the “Three Rs” program, which focused on reconstruction, rehabilitation, and reconciliation. This program aimed to rebuild war-torn areas, provide assistance to refugees and internally displaced persons, and promote national unity.
Furthermore, Gowon prioritized infrastructural development, investing in transportation networks, power generation, and educational institutions.
His government established new universities and expanded access to education, recognizing its importance in the country’s development.
However, Gowon’s time in power was not without criticism. His government faced allegations of corruption and mismanagement of resources, which led to public discontent and protests.
In 1975, while Gowon was attending an OAU summit in Uganda, a coup led by General Murtala Mohammed removed him from power.
5. General Murtala Rufai Ramat Mohammed (1975-1976)

In the history of Nigeria, the tenure of General Murtala Rufai Ramat Mohammed holds a significant place. Serving as the head of state from 1975 to 1976, his leadership left a lasting impact on the nation. Let’s take a closer look at his time in power.
He assumed office on July 29, 1975, following a military coup. His ascension to power marked a turning point in Nigeria’s history, as he aimed to address corruption, inefficiency, and abuse of power that had plagued the government.
During his brief tenure, General Mohammed implemented various reforms to improve governance and root out corruption. He set up special tribunals to investigate and prosecute corrupt officials, sending a clear message that corruption would no longer be tolerated. These efforts were seen as a positive step towards restoring public trust in the government.
Unfortunately, General Mohammed’s promising leadership was cut short on February 13, 1976, when he was assassinated in a failed coup attempt. His untimely death shocked the nation and led to a period of uncertainty and instability.
6. Major General Olusegun Obasanjo (1976-1979)

Major General Olusegun Obasanjo is a highly esteemed figure in Nigerian history, known for his remarkable leadership and significant contributions to the country’s development. Born on March 5, 1937, in Abeokuta, Nigeria, Obasanjo’s journey is an inspiration to many.
During his tenure as Head of State, Obasanjo implemented crucial reforms and initiatives to address the country’s pressing challenges. He focused on economic development, fostering social cohesion, and promoting good governance.
7. Alhaji Shehu Shagari ( 1979-1983)
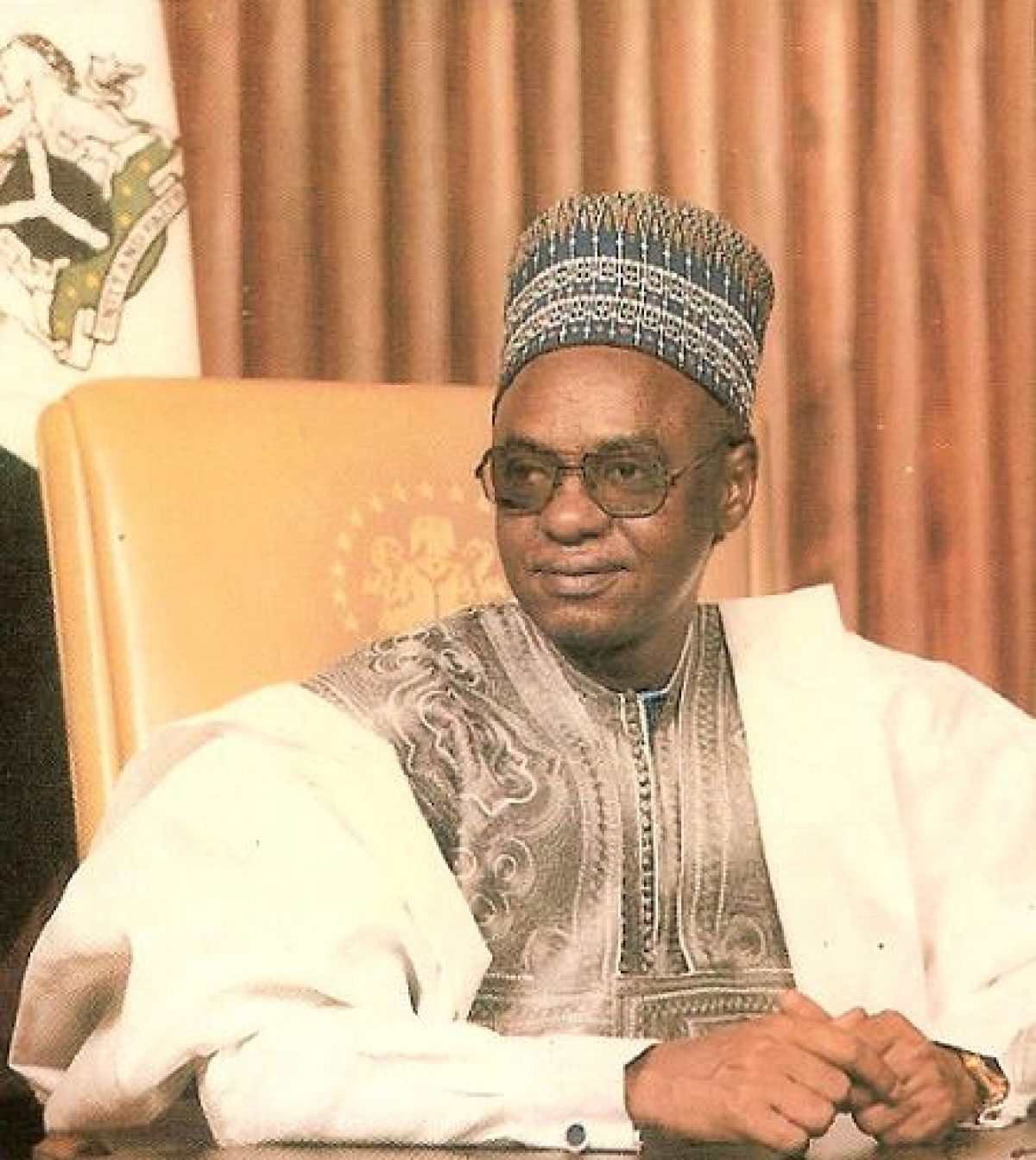

Alhaji Shehu Shagari was born on February 25, 1925, in a village of Shagari, Sokoto. Shehu is a prominent figure in Nigerian politics, left an indelible mark on the nation’s history. He emerged as a respected leader who served as the country’s first executive president.
Throughout his career, Shagari exhibited a deep commitment to democratic values and good governance. In 1979, Nigeria transitioned from military rule to civilian government, and Shagari’s exceptional leadership skills earned him the trust and support of the Nigerian people.
During his presidency, Shagari prioritized economic development and social welfare. He implemented policies aimed at reducing poverty and improving living standards for Nigerians.
Additionally, his administration focused on agricultural advancements, promoting the Green Revolution to boost food production and ensure food security for the nation.
Sadly, Shagari’s presidency was cut short in 1983 due to a military coup led by General Muhammadu Buhari. He was overthrown and subsequently placed under house arrest for three years until his release in 1986.
Even after leaving office, Shagari continued to contribute to Nigerian society. He served as an elder statesman and actively participated in various advisory roles, sharing his wealth of experience with younger generations.
8. Major General Muhammadu Buhari (1983 to 1985)

During the period from 1983 to 1985, Major General Muhammadu Buhari served as the head of state in Nigeria. Buhari, a distinguished military officer, took over the reins of power in a time of political unrest and economic challenges in the country.
Buhari’s tenure as the leader of Nigeria was marked by his strong stance against corruption and his commitment to restoring law and order. He implemented strict measures to combat corruption and instill discipline in public service. Buhari believed that addressing corruption was crucial to the nation’s development and stability.
During his time in office, Buhari also focused on improving the country’s security situation. He initiated various military operations to tackle internal threats and maintain peace within the nation. Buhari recognized the importance of a secure environment for progress and worked towards achieving stability.
Although Buhari’s time in power was relatively short, his leadership left a lasting impact on Nigeria. He established a reputation as a no-nonsense leader who prioritized accountability, discipline, and economic growth.
9. General Ibrahim Babangida (1985-1993)
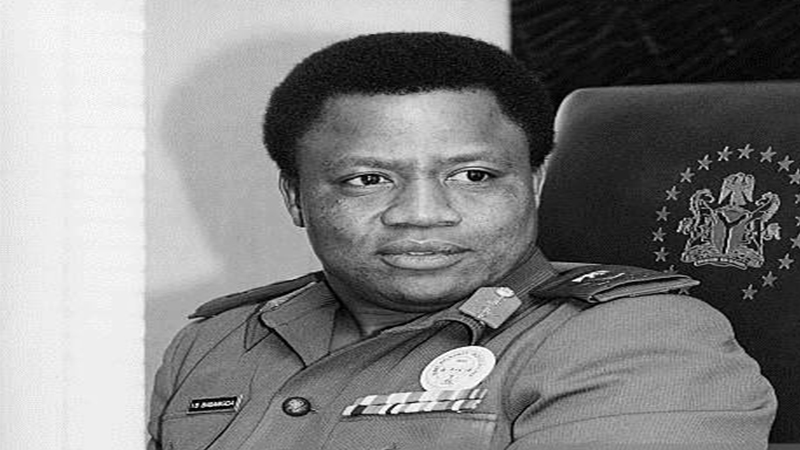

General Ibrahim Babangida is an important person in Nigerian history. He led the military government from 1985 to 1993 and had a significant impact on the country’s politics. He was born on August 17, 1941, in Minna, Niger State, and is commonly referred to as IBB.
During his tenure as the head of state, Babangida implemented significant changes in Nigeria. Babangida introduced the Structural Adjustment Program (SAP), which aimed to revitalize the country’s economy through economic liberalization and privatization.
One of Babangida’s most notable accomplishments was the establishment of the two-party system in Nigeria. He initiated a transition to democracy by creating the Social Democratic Party (SDP) and the National Republican Convention (NRC).
Babangida’s government also opened the route for private broadcasting, established the Federal Road Safety Corps, National Drug Law Enforcement Agency, and the National Directorate of Employment among others.
10. Chief Ernest Adegunle Oladeinde Shonekan (1993-1993)

Chief Ernest Adegunle Oladeinde Shonekan was born on May 9, 1936, in Lagos, Nigeria. Shonekan is a prominent Nigerian statesman, has played a significant role in the country’s political and business landscape. He has made remarkable contributions to Nigeria’s development.
Shonekan’s impact extended beyond the business sphere. In 1985, he was appointed as the Chairman of the Nigeria Stock Exchange, where he implemented significant reforms to promote transparency and accountability within the organization. His efforts led to increased investor confidence and stimulated economic growth.
Shonekan’s remarkable achievements and reputation for integrity caught the attention of Nigeria’s political elite.
In 1993, during a time of political transition, he was appointed as the interim President of Nigeria. His tenure was marked by efforts to stabilize the country and foster unity among diverse ethnic and religious groups.
Chief Ernest Shonekan has remained a symbol of excellence, integrity, and dedication to Nigeria’s progress. His passion for law, business, and politics has left an indelible mark on the country’s history. Today, he is revered as a role model for aspiring leaders and a beacon of hope for a brighter future for Nigeria.
11. General Sani Abacha (1993-1998)
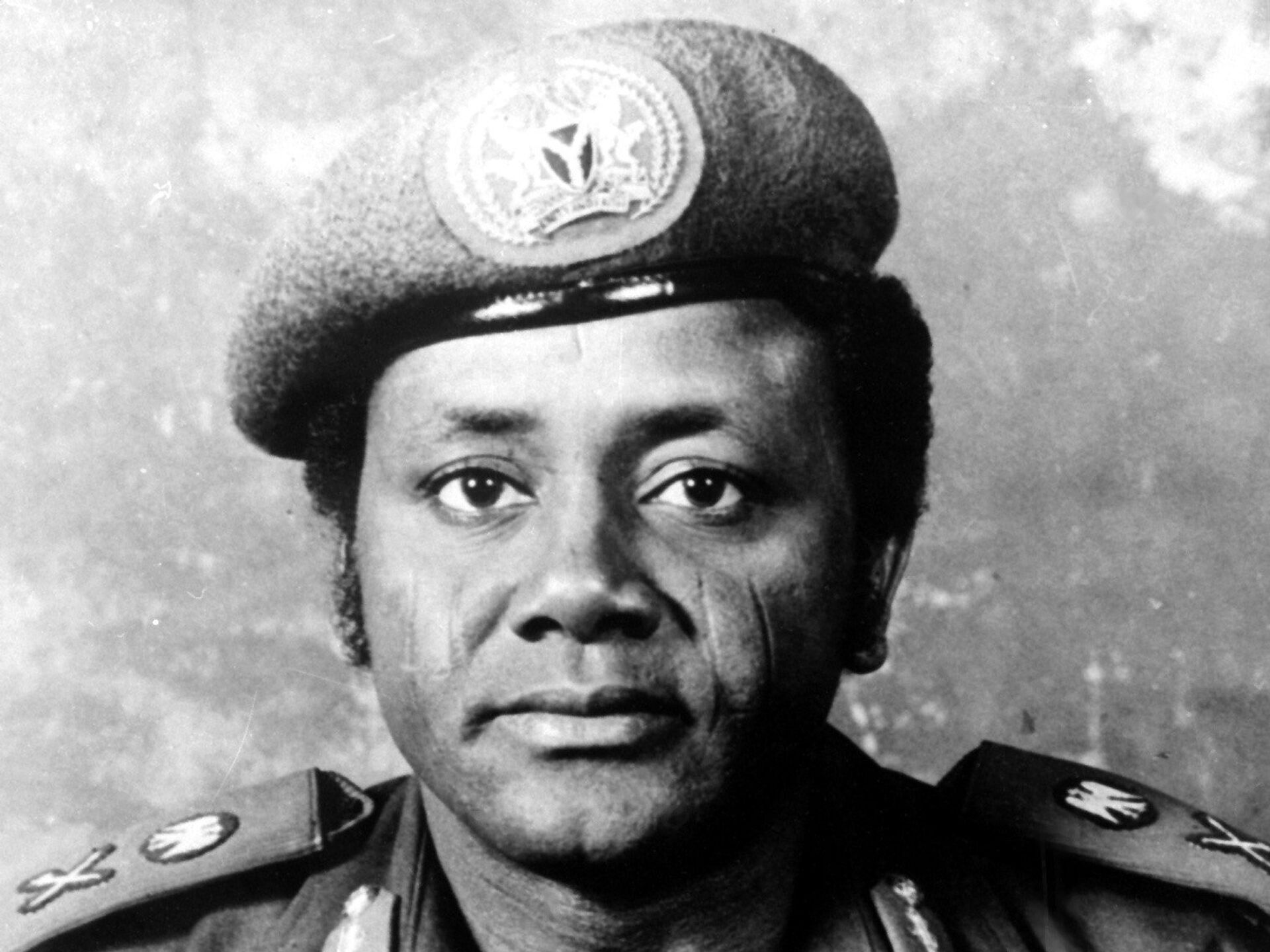

General Sani Abacha was a good figure in Nigeria’s history, serving as the country’s military leader from 1993 until his untimely death in 1998. Born on September 20, 1943, in Kano State, Abacha had a long and controversial career that left an indelible mark on Nigeria.
Abacha rose through the ranks of the Nigerian military, displaying strong leadership skills and gaining recognition for his contributions.
In November 1993, following the annulment of the presidential election, Abacha seized power through a military coup, assuming the position of Head of State and Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces.
During his time in power, Abacha’s regime faced widespread criticism for its human rights abuses and suppression of political dissent. Many activists, journalists, and political opponents were arrested and detained without trial. The regime also faced allegations of corruption, with vast amounts of public funds reportedly embezzled.
On June 8, 1998, General Sani Abacha passed away suddenly in Aso Rock, the Nigerian Presidential Villa. His death brought an end to his regime, which was succeeded by General Abdulsalami Abubakar.
12. General Abdulsalami Abubakar (1998-1999)
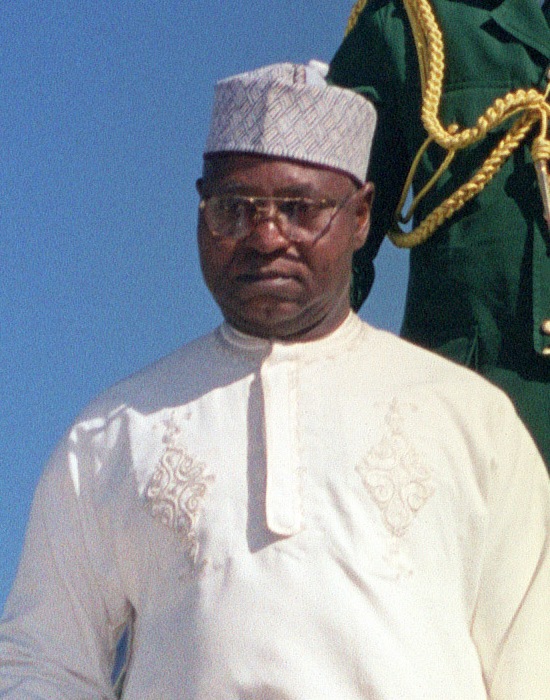
Abdulsalami Abubakar was born on June 13, 1942, in Minna, Niger State, Abdulsalami Abubakar began his military journey by joining the Nigerian Army in 1963. He dedicated over three decades of his life to serving his country, rising through the ranks to become a four-star general.
During his brief tenure from June 1998 to May 1999, General Abdulsalami Abubakar embarked on a mission to stabilize Nigeria and prepare it for a peaceful transition to civilian rule. He implemented measures to foster unity among the various ethnic and religious groups, promoting dialogue and reconciliation.
Under Abubakar’s leadership, Nigeria successfully held elections in 1999, marking the beginning of a new era of democracy in the country.
General Abdulsalami Abubakar’s contributions to Nigeria’s democratic journey and his commitment to peace have been widely recognized and honored.
He has received numerous accolades and awards, including the prestigious Mo Ibrahim Prize for Achievement in African Leadership in 2007.
13. Chief Olusegun Mathew Okikiola Aremu Obasanjo (1999-2007)
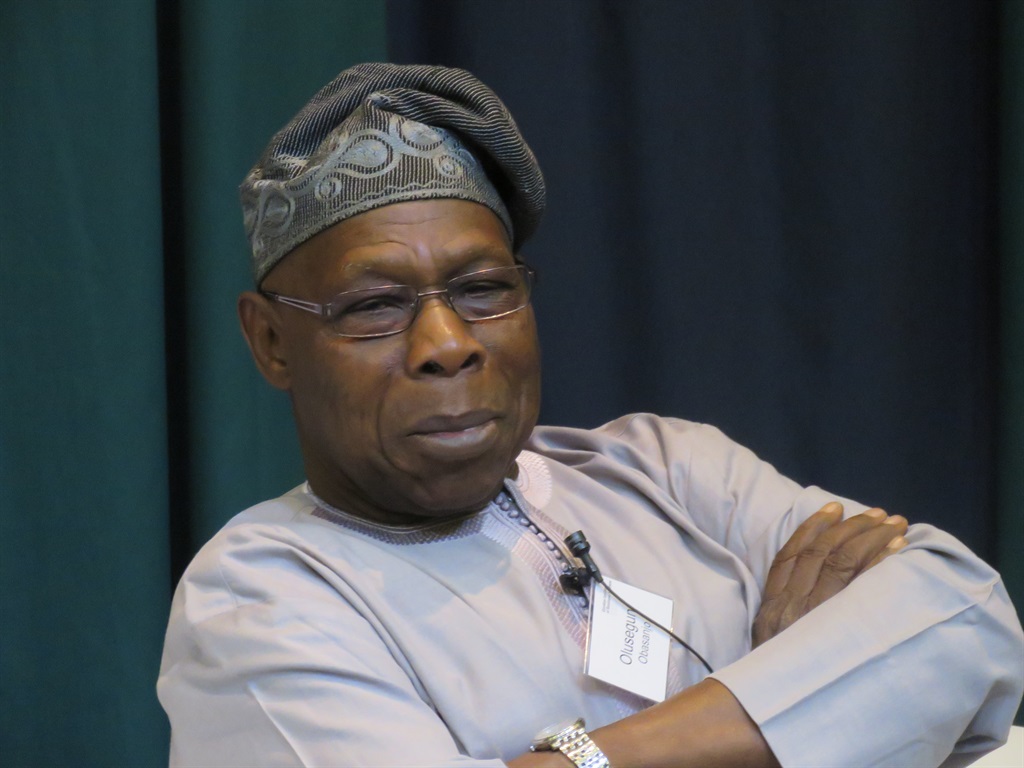

Chief Olusegun Mathew Okikiola Aremu Obasanjo served as the Nigeria President from 1999 to 2007. During his tenure, he made significant contributions to the country’s political landscape and led various initiatives to promote development and stability.
Obasanjo, a highly respected figure in Nigerian politics, was instrumental in transitioning the country from military rule to democracy. His election as president in 1999 marked the first peaceful handover of power between civilian administrations in Nigeria since the 1960s.
Under Obasanjo’s leadership, Nigeria experienced notable improvements in various sectors. He focused on expanding access to education, healthcare, and basic amenities for all Nigerians.
Obasanjo’s tenure left a lasting impact on Nigeria’s political and socio-economic landscape.
Chief Olusegun Mathew Okikiola Aremu Obasanjo remains an influential figure in Nigerian politics, with his legacy serving as a reminder of the potential for positive change and progress in the nation.
14. President Umaru Musa Yar’Adua (2007-2010)
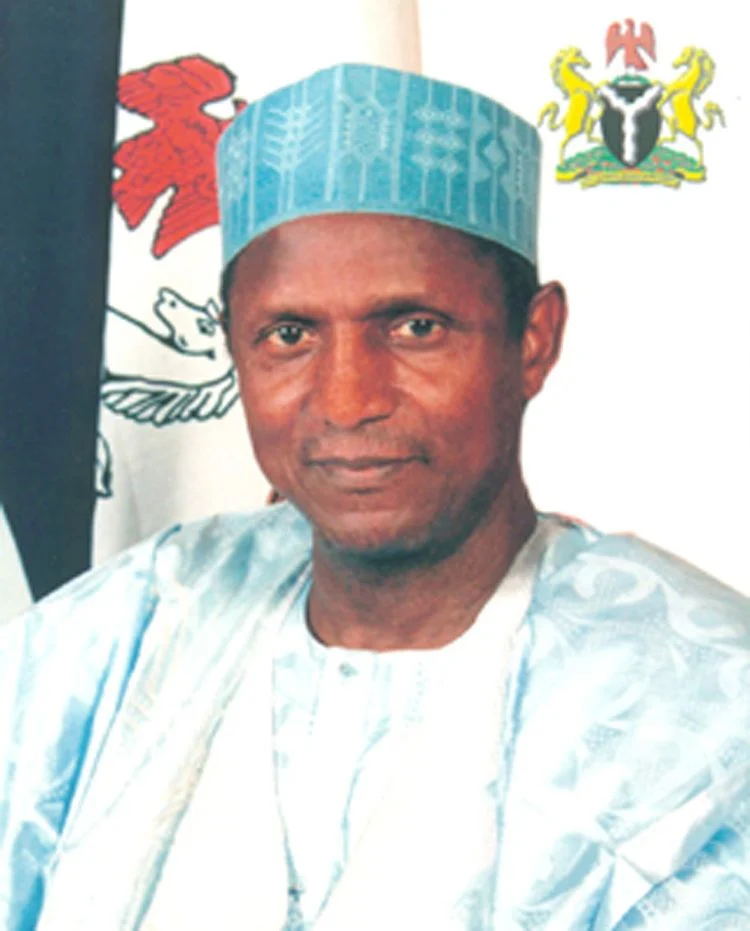

Umaru Musa Yar’Adua was born on August 16, 1951, in Katsina State, Nigeria. He hailed from a respected political family, with his father, Musa Yar’Adua, having served as a Minister.
Umaru Musa Yar’Adua served as the President of Nigeria from 2007 to 2010. During his presidency, launched programs to tackle poverty and promote access to quality education and healthcare. His administration prioritized the provision of basic amenities and infrastructure, such as electricity and clean water, to improve the standard of living for all Nigerians.
One of the key accomplishments of Yar’Adua’s presidency was his commitment to tackling corruption head-on. He established the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC) to combat corruption effectively. He implemented reforms to enhance transparency and accountability within the government, aiming to eradicate corruption and promote good governance.
Yar’Adua’s leadership style was characterized by his humility, compassion, and inclusivity. He engaged in constructive dialogue with various stakeholders, including opposition parties, civil society organizations, and international partners, to foster consensus and collaboration.
Tragically, Yar’Adua’s presidency was cut short due to his untimely death in 2010. President Umaru Musa Yar’Adua will always be remembered as a leader who dedicated himself to serving the Nigerian people, striving for progress, and leaving behind a legacy of positive change.
15. Goodluck Ebele Azikiwe Jonathan (2010-2015)
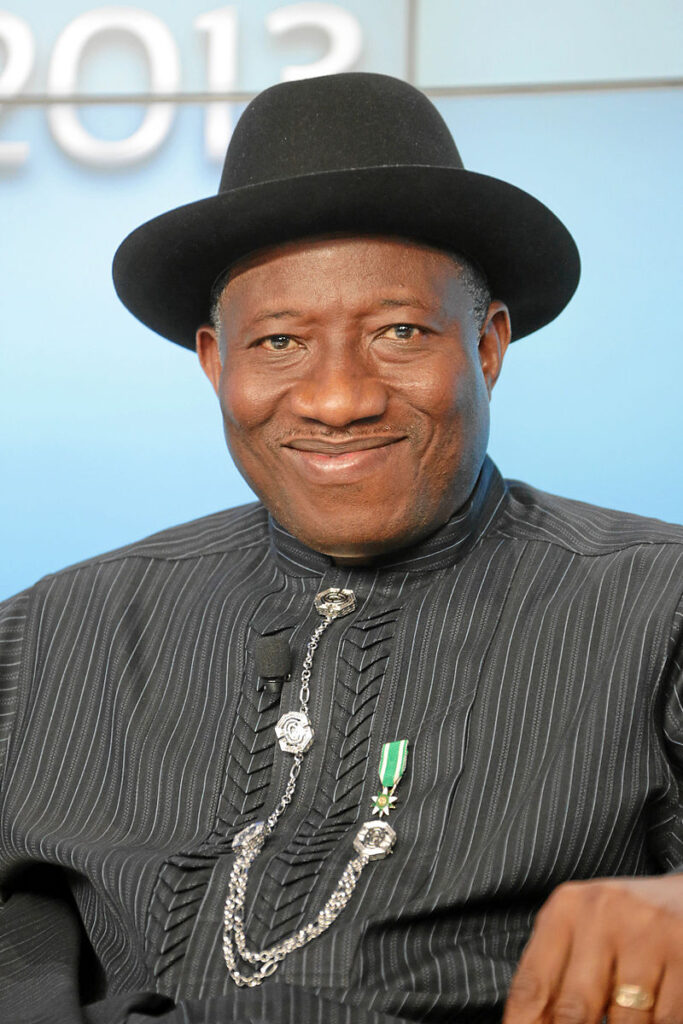

Goodluck Ebele Azikiwe Jonathan, commonly known as Goodluck Jonathan, is a Nigerian politician who served as the President of Nigeria from 2010 to 2015. He was born on November 20, 1957, in Ogbia, Bayelsa State, Nigeria.
In 2010, Jonathan assumed the presidency after the unfortunate passing of President Umaru Musa Yar’Adua. As President, Jonathan focused on addressing the challenges faced by Nigeria, such as corruption, power shortages, and terrorism.
He implemented various policies aimed at promoting transparency, economic growth, and social development.
During his presidency, Jonathan played a significant role in the restoration of democratic governance in Nigeria. He facilitated the peaceful transition of power after losing the 2015 presidential election, setting a positive precedent for Nigerian democracy.
Throughout his life, Jonathan has advocated for peaceful elections, democratic values, and conflict resolution in Nigeria and across the African continent.
After leaving office, Jonathan continued to be involved in international diplomacy and conflict resolution efforts.
Today, Jonathan continues to be a respected figure in Nigeria and beyond, admired for his statesmanship and his efforts to promote peace and democracy
16. President Muhammadu Buhari (2015-2023)

Muhammadu Buhari, a Nigerian politician, served as the president of Nigeria from 2015 to 2023. He was also a retired Nigerian army major general and the country’s military head of state from 1983 to 1985, after taking power in a military coup.
During his time in office, Buhari implemented various policies and initiatives aimed at addressing the country’s challenges and promoting development.
One of the key focuses of President Buhari’s administration was tackling corruption. He launched an anti-corruption campaign that aimed to root out corruption in both public and private sectors.
Another area of focus for President Buhari was the economy. Nigeria is Africa’s largest economy, but it faces numerous economic challenges, including high unemployment rates and overdependence on oil revenues.
Throughout his presidency, President Buhari faced both support and criticism from the Nigerian population.
17. Chief Bola Ahmed Adekunle Tinubu (Present)
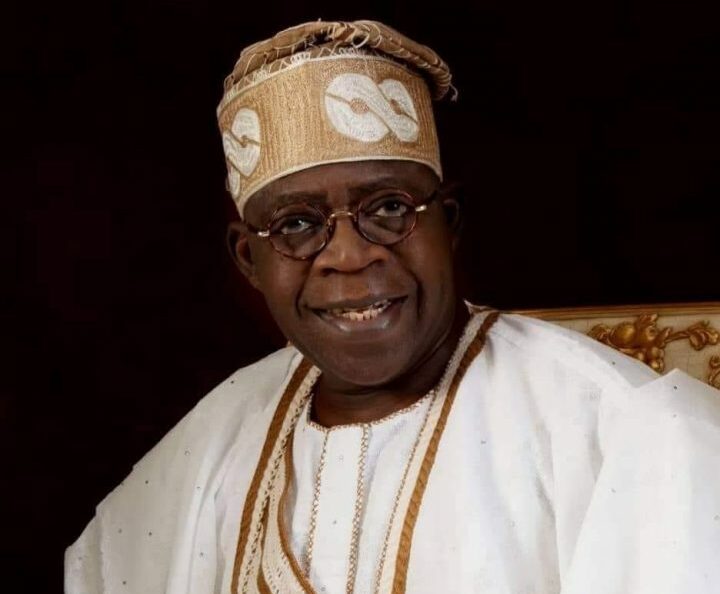

Bola Ahmed Adekunle Tinubu, born on March 29, 1952, is a Nigerian politician. He currently serves as the 16th president of Nigeria. From 1999 to 2007, he was the governor of Lagos State, and prior to that, he served as a senator for Lagos West during the Third Republic.
Tinubu officially became the President of Nigeria on May 29, 2023. The Chief Justice of Nigeria, Olukayode Ariwoola, will swear him in at 10 AM (WAT) during an inauguration ceremony at Eagle Square in the Federal Capital Territory.
Tinubu’s government has overcome legal challenges from the opposition after the March election and is widely accepted both domestically and internationally. Many heads of state and government are expected to attend the swearing-in ceremony.
Prior to his presidency, Tinubu received the highest national honor, the Grand Commander of the Order of the Federal Republic, from his predecessor, Muhammadu Buhari. His Vice President, Kashim Shettima, was honored with the second highest award, the Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger, on May 25.
CONCLUSION:
Nigerian politics has witnessed a myriad of challenges and significant progress in recent years. Challenges in Nigerian Politics such as Corruption, Ethnic and Religious Divisions, Electoral Integrity, Inadequate and Infrastructure.
There are also Progress in Nigerian Politics which include Democratic Transition, Economic Reforms, Anti-Corruption Efforts, Infrastructural Development and Youth Engagement
Nigeria has great potential for future growth and development due to its abundant natural resources, a growing population and market, infrastructure development, economic reforms and diversification, and its regional and international influence.
